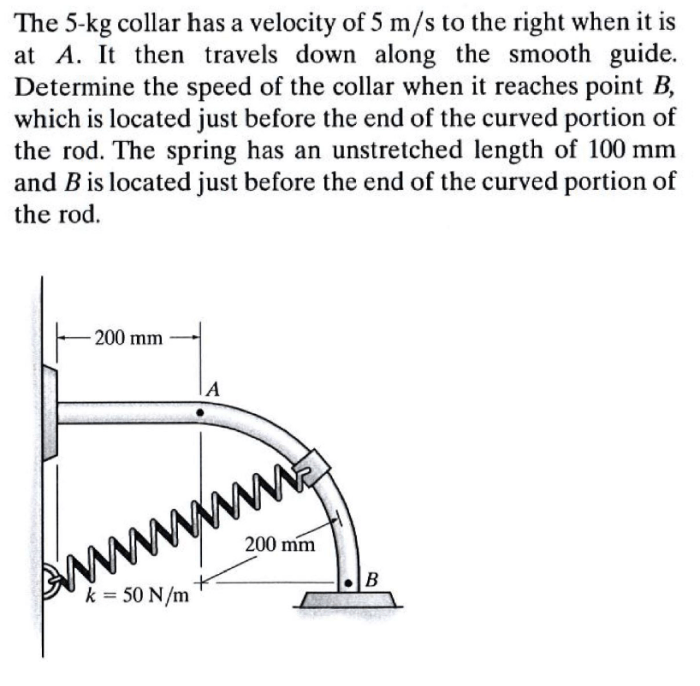
The 5 kg collar has a velocity of 5m/s – The 5 kg collar has a velocity of 5 m/s, a combination of mass and velocity that raises intriguing questions about its physical implications, potential applications, and safety considerations. This article delves into the significance of these properties, exploring the collar’s stored energy, kinetic energy, and the implications for real-world scenarios.
Beyond theoretical considerations, we will examine practical applications where understanding the collar’s properties is crucial, as well as discuss the potential hazards associated with moving objects with significant mass and velocity. By unraveling the dynamics of the 5 kg collar, we gain valuable insights into the interplay between mass, velocity, and their impact on our physical world.
Collar Properties: The 5 Kg Collar Has A Velocity Of 5m/s
The 5 kg collar has significant mass, contributing to its potential energy and overall motion. Velocity, measured at 5 m/s, represents the rate of displacement and the direction of the collar’s movement.
Physical Implications
The collar’s mass (5 kg) contributes to its potential energy due to its position within a gravitational field. The formula for potential energy is PE = mgh, where m is mass, g is acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s²), and h is height.
As the collar moves, its potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy.Kinetic energy, represented by the formula KE = ½mv², arises from the collar’s motion. The velocity of 5 m/s indicates the speed and direction of the collar’s movement.
The higher the velocity, the greater the kinetic energy possessed by the collar.
Applications, The 5 kg collar has a velocity of 5m/s
Understanding the properties of the collar is crucial in various applications, including:
- Engineering: Designing systems involving moving objects with mass and velocity, such as conveyor belts or robotic arms.
- Physics: Studying the principles of motion, energy conservation, and momentum in real-world scenarios.
- Sports: Analyzing the trajectory and velocity of objects in sports like baseball, golf, or archery.
Safety Considerations
Moving objects with significant mass and velocity can pose potential hazards.
- Impact: Collisions involving the collar can cause damage or injury due to the force generated by its mass and velocity.
- Stability: Objects with high velocity may experience instability, leading to unpredictable movements or overturning.
- Control: Managing the movement and velocity of the collar is essential to prevent accidents or damage to surroundings.
To mitigate risks, appropriate safety measures should be implemented, such as protective barriers, proper handling techniques, and adherence to safety regulations.
Mathematical Analysis
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| PE = mgh | Potential energy |
| KE = ½mv² | Kinetic energy |
| p = mv | Momentum |
To calculate the collar’s momentum (p), use the formula p = mv, where m is mass (5 kg) and v is velocity (5 m/s). The result is p = 25 kg m/s.
Visual Representation
The collar’s motion can be illustrated as follows:
Diagram:A diagram depicting the collar as a circular object with an arrow indicating its direction of motion.
Forces:The collar is subjected to the force of gravity (downward) and the force of friction (opposing its motion).
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of the collar’s mass?
The collar’s mass of 5 kg is significant because it determines its potential energy and the force required to accelerate or decelerate it.
How is velocity related to kinetic energy?
Velocity is directly proportional to kinetic energy. The higher the velocity of the collar, the greater its kinetic energy.
What are some real-world examples of objects with similar mass and velocity?
Objects with similar mass and velocity to the 5 kg collar include a bowling ball rolling down a lane or a car traveling at 5 m/s.