Which attribution type algorithmically evaluates individual customer paths – Algorithmic Evaluation: Assessing Individual Customer Paths delves into the realm of attribution modeling, exploring the specific attribution type that leverages algorithms to evaluate the unique journeys of individual customers. This approach empowers marketers with granular insights into the effectiveness of their campaigns, enabling them to optimize their strategies for maximum impact.
Algorithmic evaluation offers a sophisticated method for tracking customer behavior, providing a comprehensive understanding of touchpoints and interactions that influence purchasing decisions. By harnessing the power of data and statistical models, marketers can gain valuable insights into the factors that drive conversions, ultimately enhancing the customer experience and driving business growth.
Attribution Types
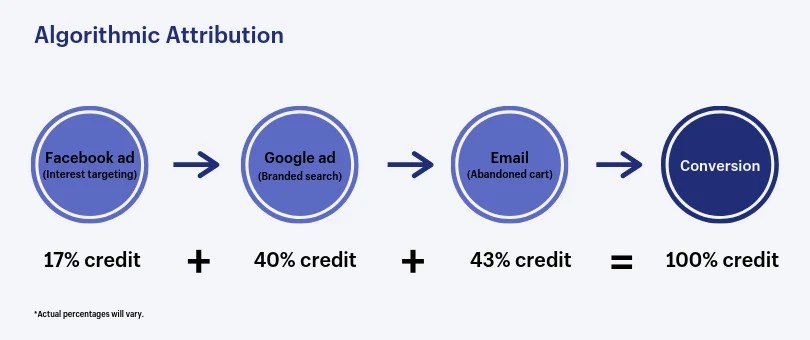
Attribution models are used to assign credit for conversions to different marketing touchpoints. There are a number of different attribution models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Single-Touch Attribution
- Gives all the credit for a conversion to the last touchpoint that the customer interacted with before converting.
- Simple to implement and understand.
- Can overvalue the importance of last-touch channels, such as paid search.
Multi-Touch Attribution
- Distributes credit for a conversion across all of the touchpoints that the customer interacted with before converting.
- More complex to implement and understand than single-touch attribution.
- Can provide a more accurate picture of the customer journey.
Time-Decay Attribution
- Gives more credit to touchpoints that occurred closer to the time of conversion.
- Can be useful for tracking the impact of short-term marketing campaigns.
- Can be difficult to determine the appropriate time decay curve.
Position-Based Attribution
- Gives equal credit to all touchpoints that occurred in a specific position in the customer journey.
- Simple to implement and understand.
- Can overvalue the importance of early-stage touchpoints, such as brand awareness.
Algorithmic Evaluation of Individual Customer Paths
Algorithmic evaluation can be used to assess the effectiveness of individual customer paths. This can be done by tracking the customer’s journey through the marketing funnel and identifying the touchpoints that had the most impact on the customer’s decision to convert.
Path Analysis
Path analysis is a technique that can be used to identify the most common paths that customers take through the marketing funnel.
Markov Chains
Markov chains are a type of statistical model that can be used to predict the probability of a customer taking a particular path through the marketing funnel.
Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation is a technique that can be used to simulate the customer journey and identify the touchpoints that have the greatest impact on conversion.
Measuring Customer Engagement
Customer engagement is a measure of how active and involved customers are with a brand. There are a number of different metrics that can be used to measure customer engagement, such as:
- Website traffic
- Social media engagement
- Email open rates
- Customer reviews
- Purchase frequency
These metrics can be used to track the success of marketing campaigns and identify areas for improvement.
Personalization and Customer Experience
Personalization is the practice of tailoring marketing messages and experiences to the individual customer. This can be done by using data to segment customers into different groups and then creating targeted marketing campaigns for each group.
Benefits of Personalization, Which attribution type algorithmically evaluates individual customer paths
- Increased customer engagement
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Increased sales
Methods of Personalization
- Segmentation
- Behavioral targeting
- Contextual targeting
Cross-Channel Attribution: Which Attribution Type Algorithmically Evaluates Individual Customer Paths
Cross-channel attribution is the practice of tracking customer journeys across multiple channels. This can be done by using cookies, device fingerprinting, or other tracking technologies.
Benefits of Cross-Channel Attribution
- Improved understanding of the customer journey
- More accurate attribution of marketing spend
- Improved marketing campaign optimization
Methods of Cross-Channel Attribution
- Last-touch attribution
- First-touch attribution
- Multi-touch attribution
- Time-decay attribution
Future of Attribution
The future of attribution modeling is likely to be driven by the continued growth of digital marketing and the increasing availability of data.
New Technologies
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Machine learning (ML)
- Big data
These technologies will enable marketers to develop more sophisticated and accurate attribution models that can provide a better understanding of the customer journey.
Query Resolution
What are the advantages of using algorithmic evaluation for individual customer paths?
Algorithmic evaluation provides granular insights into customer behavior, enabling marketers to identify the most influential touchpoints and optimize campaigns accordingly.
How does algorithmic evaluation differ from traditional attribution models?
Algorithmic evaluation leverages statistical models and data analysis to assess individual customer journeys, while traditional models often rely on predefined rules or heuristics.
What are some examples of how algorithmic evaluation can be used to improve marketing campaigns?
Algorithmic evaluation can help marketers identify high-value customer segments, optimize content for specific touchpoints, and personalize messaging based on individual customer behavior.