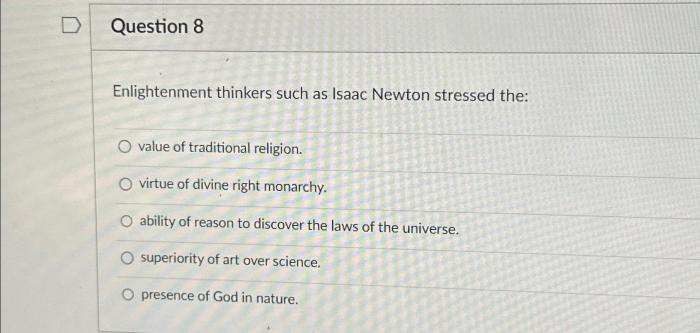
Enlightenment thinkers such as Isaac Newton stressed the importance of empirical observation and experimentation in scientific inquiry. Their ideas laid the foundation for modern scientific thought and continue to influence our understanding of the natural world.
This article explores the contributions of enlightenment thinkers to the development of modern science, with a particular focus on Isaac Newton’s groundbreaking discoveries in physics.
Enlightenment Thinkers and Their Impact on Modern Science

Enlightenment thinkers played a pivotal role in the development of modern scientific thought. They emphasized the importance of empirical observation, experimentation, and reason in understanding the natural world.
Among the most influential enlightenment thinkers were Isaac Newton, John Locke, and René Descartes. Newton’s groundbreaking discoveries in physics and mathematics laid the foundation for classical mechanics and optics. Locke’s empiricist philosophy emphasized the role of experience in acquiring knowledge, while Descartes’ rationalist philosophy stressed the importance of logical reasoning.
The ideas of these thinkers profoundly influenced the scientific method and the way scientists approached the study of nature. They helped to establish the principles of objectivity, skepticism, and the pursuit of knowledge through systematic inquiry.
Isaac Newton’s Contributions to Enlightenment Thought
Isaac Newton was one of the most influential scientists of all time. His discoveries in physics and mathematics revolutionized our understanding of the natural world.
Newton’s key scientific discoveries include the laws of motion, the law of universal gravitation, and the development of calculus. His laws of motion describe the relationship between an object’s mass, velocity, and acceleration, while his law of universal gravitation explains the force of attraction between any two objects with mass.
Newton’s emphasis on empirical observation and experimentation was a major departure from the traditional Aristotelian approach to science. He believed that scientific knowledge should be based on evidence gathered through careful observation and experimentation, rather than on abstract reasoning or speculation.
The Influence of Enlightenment Ideas on Society
Enlightenment ideas had a profound impact on political, economic, and social thought. They helped to shape the American Revolution and the French Revolution, and their legacy continues to influence modern society.
Enlightenment thinkers believed in the natural rights of individuals, including the right to life, liberty, and property. They also believed in the importance of limited government and the separation of powers. These ideas were reflected in the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution of the United States.
Enlightenment ideas also influenced economic thought. Adam Smith, a Scottish economist, argued that free markets and limited government intervention would lead to economic growth and prosperity. His ideas were influential in the development of capitalism.
Comparative Analysis of Enlightenment Thinkers
| Name | Major Works | Key Ideas | Impact on Science or Society |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isaac Newton | Principia Mathematica, Opticks | Laws of motion, law of universal gravitation, calculus | Revolutionized physics and mathematics |
| John Locke | Two Treatises of Government, An Essay Concerning Human Understanding | Empiricism, natural rights, limited government | Influenced political thought and the American Revolution |
| René Descartes | Discourse on Method, Meditations on First Philosophy | Rationalism, Cartesian doubt, cogito ergo sum | Influenced philosophy and the development of mathematics |
Visual Representation of Enlightenment Ideas
This image represents Newton’s discovery of the law of universal gravitation.
This image represents Locke’s empiricist philosophy, which states that the mind is a blank slate at birth and that all knowledge is acquired through experience.
This image represents Descartes’ rationalist philosophy, which states that the only thing we can be certain of is that we exist.
FAQ Resource: Enlightenment Thinkers Such As Isaac Newton Stressed The
Who were the key enlightenment thinkers?
Some of the most influential enlightenment thinkers included Isaac Newton, John Locke, and René Descartes.
What were the major contributions of enlightenment thinkers to science?
Enlightenment thinkers made significant contributions to the development of modern science, including the scientific method, the laws of motion, and the theory of gravity.
How did enlightenment ideas influence society?
Enlightenment ideas had a profound impact on society, shaping political, economic, and social thought. They also played a major role in the American and French Revolutions.